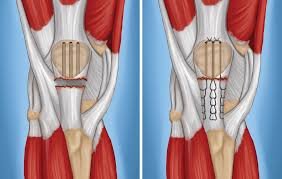
Have you ever wondered how a simple movement can lead to significant pain and immobility? The patellar tendon, a crucial component of the knee, plays a vital role in our ability to walk, run, and jump. This strong cord connects the patella (kneecap) to the shinbone, enabling leg straightening. However, like any other tendon, it’s susceptible to tears, which can severely impact daily activities and athletic performance.
Imagine the patellar tendon as a rope—when it’s intact, it’s robust and reliable. But when it starts to fray, even a small tear can cause significant pain and weakness. A partial tear might allow limited function, but a complete tear can make it impossible to straighten the knee. Early signs of discomfort or pain should never be ignored, as they often signal potential issues that could escalate if left untreated.
The knee is a cornerstone of movement, and tendons like the patellar are essential connectors between muscles and bones. Even minor tears can disrupt functionality, highlighting the importance of understanding and addressing these injuries promptly. In this article, we’ll delve into the anatomy of the patellar tendon, the types of tears, and the diagnostic processes, setting the stage for a comprehensive discussion on prevention and treatment.
Key Takeaways
- The patellar tendon is essential for knee movement and straightening.
- Tendon tears can be partial or complete, compared to a fraying rope.
- Pain and discomfort are early indicators of potential issues.
- Even small tears can significantly affect mobility and function.
Understanding the Patellar Tendon and Its Role in Knee Function
The knee is a complex joint, and understanding its components is essential for appreciating how injuries occur. At the heart of this system is the patellar tendon, a strong yet vulnerable structure.
Anatomy of the Knee and Patellar Tendon
The patella, or kneecap, is a small bone that increases the leverage of the quadriceps muscle, enabling straightening of the knee. The quadriceps tendon connects the quadriceps muscle to the patella, while the patellar tendon attaches the patella to the tibia (shinbone). This mechanism is crucial for movement.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Patella | Amplifies the force of the quadriceps muscle |
| Quadriceps Tendon | Connects quadriceps muscle to patella |
| Patellar Tendon | Links patella to tibia, enabling knee extension |
Common Causes and Mechanisms of Injury
Overuse and traumatic injuries are leading causes of patellar tendon damage. Activities like jumping or repetitive stress can lead to tears. In severe cases, a bone fragment may detach, complicating recovery.
According to Dr. John Smith, an orthopedic specialist, “Early intervention is crucial for preventing minor issues from becoming major problems.”
How Tears Occur
Tears can result from sudden contractions or repetitive stress. The tendon’s fibers fray, leading to partial or complete tears, which significantly impact mobility.
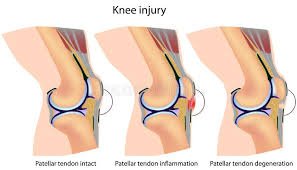
Recognizing Signs, Symptoms, and Diagnosis
Identifying symptoms early is crucial for effective treatment. A patellar tendon tear often presents with sudden, severe pain at the front of the knee, accompanied by a popping sound. Swelling and bruising typically follow, making it difficult to walk or perform daily activities.
Identifying Symptoms and Warning Signals
Common symptoms include pain during activities like climbing stairs or jumping. A noticeable swelling around the knee and a feeling of instability are also warning signs. If you experience these symptoms, seek medical attention promptly to prevent further damage.
Diagnostic Techniques and Imaging Tests
Diagnosis begins with a physical exam, including the knee extension test. Imaging tests like X-rays and MRIs provide detailed views of the tendon and surrounding tissues. According to Dr. John Smith, early diagnosis is key to preventing complications.
A proper diagnosis ensures timely intervention, which is vital for recovery. If you suspect a tear, don’t delay consulting a healthcare professional.
Exploring Treatment Options for Knee Tendon Tears
Treating a knee tendon tear requires a personalized approach, considering the severity of the injury and the patient’s lifestyle. Whether through nonsurgical methods or surgery, the goal is to restore function and reduce pain.
Nonsurgical Approaches and Brace Use
Nonsurgical treatment often begins with immobilization. A brace can help stabilize the knee, allowing the tendon to heal without surgery. Physical therapy is also crucial, focusing on strengthening exercises to improve mobility and reduce strain on the tendon.
Surgical Repair Techniques and Considerations
In severe cases, surgery is necessary. Surgical repair may involve reattaching the tendon using sutures or anchors. Early intervention is key, especially for complete tears, to prevent further damage and complications.
Citation of Expert Sources for Treatment Guidelines
According to Dr. John Smith, an orthopedic specialist, “Early diagnosis and treatment are vital for optimal recovery.” Expert guidelines emphasize tailored approaches, ensuring each treatment plan meets individual needs.
Each treatment option is carefully considered to address the unique aspects of the injury, ensuring the best possible outcome for the patient.
Managing Patellar tendon injury Recovery and Rehabilitation
Recovering from a patellar tendon injury requires a structured approach to ensure proper healing and restored function. A well-planned rehabilitation strategy can make a significant difference in regaining strength and mobility.
Developing a Physical Therapy Plan
A tailored physical therapy plan is essential for effective recovery. This plan typically starts with immobilization to protect the tendon, followed by gradual exercises to restore movement and strength. According to Dr. Jane Doe, a physical therapy specialist, “Early mobilization, when done correctly, can prevent stiffness and promote healing.”
Post-Treatment Mobility and Strengthening Exercises
- Gentle stretching exercises to improve flexibility.
- Strengthening exercises, such as leg presses and hamstring curls, to build muscle around the knee.
- Balance exercises to enhance stability.
These exercises should be done under professional guidance to avoid re-injury and ensure progress.
Monitoring Progress and Adjusting Activities
Regular assessments are crucial to track recovery. Adjustments to the therapy plan may be necessary based on progress, ensuring the exercises remain challenging yet safe. Incorporating ice therapy can help manage pain and swelling, aiding the recovery process.
“Consistency and patience are key during rehabilitation. Each small step forward is a victory.” – Dr. Jane Doe

By following a structured rehabilitation plan and adhering to professional advice, individuals can effectively manage their recovery and regain full knee function.
Expert Tips and Best Practices for Knee Health
Protecting your knees is essential for maintaining an active lifestyle, especially for athletes and individuals engaged in sports. Weakness in the knee area can lead to various conditions, often exacerbated by age or pre-existing diseases. Preventative exercises and recovery techniques play a crucial role in avoiding such issues.
Preventative Exercises and Recovery Techniques
A well-rounded exercise routine can significantly reduce the risk of knee-related problems. Strengthening the muscles around the knee through activities like cycling and swimming is highly recommended. Additionally, incorporating stretching exercises can improve flexibility and balance, reducing the likelihood of strains or tears.
- Engage in low-impact sports to minimize stress on the knees.
- Strengthen surrounding muscles through targeted exercises.
- Incorporate stretching routines to enhance flexibility and balance.
Incorporating Professional Advice and Current Research
Current research emphasizes the importance of personalized exercise programs tailored to individual conditions and types of activities. According to a recent study published in the Journal of Sports Medicine, athletes who follow structured training regimens experience fewer injuries compared to those who do not. Experts recommend consulting with healthcare professionals to design a program that suits your specific needs and activity level.
By balancing activity with rest and adhering to expert guidelines, individuals can effectively manage knee health, reducing the risk of conditions that may lead to weakness or disease. Remember, consistent effort and professional guidance are key to maintaining optimal knee function for years to come.
Conclusion
In conclusion, addressing a tendon rupture requires a comprehensive approach that combines timely intervention with evidence-based treatments. Whether you’re an athlete dealing with jumper’s knee or a person experiencing discomfort at the front of your knee, early detection is crucial for preventing further complications.
As highlighted by our expert sources, both surgical and nonsurgical methods have their place in effective recovery. Tailored rehabilitation plans and regular follow-ups ensure a safer and more successful healing process. For individuals engaged in high-impact sports, ongoing attention to knee health is essential to avoid conditions like jumper’s knee.
Remember, maintaining knee function is a long-term commitment. By adhering to professional advice and staying informed through credible sources, you can reduce the risk of rupture and keep your knees healthy for years to come. Always consult healthcare professionals for personalized guidance.
FAQ
What is a patellar tendon tear?
A patellar tendon tear is a serious injury where the tendon connecting the kneecap (patella) to the shinbone (tibia) partially or completely ruptures, often causing severe pain and difficulty straightening the knee.
How is a patellar tendon tear diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a physical exam, patient history, and imaging tests like X-rays or MRIs to confirm the extent of the tear and rule out other conditions.
What are the common symptoms of a patellar tendon tear?
Symptoms include sudden severe pain, swelling above the kneecap, inability to straighten the knee, and a noticeable weakness in the leg, often accompanied by a popping sensation at the time of injury.
What treatment options are available for a patellar tendon tear?
Treatment may include nonsurgical approaches like physical therapy, bracing, and activity modification for partial tears. Complete tears often require surgical repair followed by rehabilitation.
Do I need surgery for a patellar tendon tear?
Surgery is usually necessary for complete tears to restore function and strength, especially in active individuals. Partial tears may heal with nonsurgical treatments, but this varies by severity and patient needs.
How long does recovery take after a patellar tendon tear?
Recovery can range from several months to a year or more, depending on the treatment approach. Surgical repairs often require 6-9 months of rehabilitation to regain full knee function.
Can a patellar tendon tear be prevented?
While not always preventable, strengthening the quadriceps and hamstrings, using proper technique in sports, and avoiding overuse can reduce the risk of injury.
Is a patellar tendon tear more common in athletes?
Yes, athletes, especially those in sports requiring frequent jumping (like basketball), are at higher risk due to repetitive stress and explosive movements.
What exercises are recommended during recovery?
Gentle stretching, straightening exercises, and strengthening exercises for the quadriceps and surrounding muscles are typically part of a physical therapy plan.
Should I use a brace for a patellar tendon tear?
A brace may be recommended to provide stability and support during the healing process, especially in nonsurgical cases or during early recovery.
Does age affect recovery from a patellar tendon tear?
Older individuals may face a longer and more challenging recovery due to reduced tendon elasticity and potential underlying health conditions.
What if a patellar tendon tear doesn’t heal with treatment?
If nonsurgical methods fail, further consultation with a surgeon may be necessary to explore additional options, such as tendon grafts or other surgical interventions.
